Official procedures for limiting natural gas consumption
Over the last few months, the natural gas market in Poland and Europe has been affected by historic price fluctuations, and the situation in Ukraine demands attention to the continuity of gas supplies from abroad. In the context of ensuring security of gas supply to end-users, we point to the potential for introduction of restrictions on natural gas consumption.
Coinciding technological and economic factors may justify limitations on natural gas consumption. From the technological perspective, it is necessary to ensure the proper functioning of the gas system in view of the reduced supply of the commodity and the low levels in gas storage facilities in Europe. From the economic perspective, we are faced with high natural gas prices in European markets.
Therefore, in the event of a threat to the state’s fuel security or an unpredicted increase in natural gas consumption by customers, the Polish Council of Ministers may introduce “degrees” of natural gas supply, exercising its powers under the Stocks Act (Act on Stocks of Crude Oil, Petroleum Products and Natural Gas and on Rules for Handling Situations of State Fuel Security Threat and Petroleum Market Disturbances on Stocks) and the executive regulation issued under that act (Regulation of the Council of Ministers of 17 February 2021 on the Manner and Procedure for Introducing Restrictions on Consumption of Natural Gas). In simple terms, this means the ability for the government to impose top-down restrictions on natural gas consumption.
Which customers may be affected by natural gas consumption restrictions?
Only selected businesses may be required to significantly reduce their use of natural gas. Primarily, the restrictions may affect businesses whose ordered contracted capacity exceeds 710 kWh/h. However, easing of this mechanism is provided for a group of entities engaged in a broad range of activities for the public good.
These restrictions are implemented depending on the “intensity” of the threat to the natural gas market. It has a direct bearing on the magnitude of the constraints, defined as power supply degrees, from one through twelve, according to the following rules.

Thus, at the severest degrees, it cannot be ruled out that a given business will be barred from consuming natural gas altogether.
Who manages the introduction of power supply degrees?
There is a formal procedure for introduction of power supply degrees. The Minister of Energy submits a formal application to the Council of Ministers, which may introduce specific power supply degrees through an executive regulation, guided by the importance of the customers involved for the economy and the functioning of the state.
Plans to introduce restrictions
However, from the point of view of each business, the individual plans for introducing restrictions in the supply of natural gas are the most important. Businesses should derive their obligations from the data included in these documents.
These plans, prepared by distribution system operators, specify the maximum hourly and daily amounts of natural gas consumption by specific customers connected to the operator’s network, for selected supply degrees. Significantly, businesses are required to inform the operator annually of the minimum amount of natural gas necessary to be consumed at power supply degree 10. Only then can the operator determine the natural gas consumption values corresponding to the power supply degrees.
Sanctions for failure to comply with natural gas consumption restrictions
When restrictions are imposed, failure to comply with the restrictions exposes the business to significant fines calculated in relation to the volume of natural gas consumed.
A restriction mechanism was most recently introduced in 2015. Although at that time it concerned restrictions in the supply and consumption of electricity, the mechanism is largely analogous to the natural gas market. Many businesses, unaware of the mechanisms introduced, failed to adjust their electricity consumption to the capacity imposed at the time. As a consequence, administrative proceedings were initiated by the regulator against thousands of businesses, seeking to impose fines for non-compliance with the restrictions. In some cases, the fines ran as high as several million zlotys. Our experience shows that in the situation of limiting natural gas supplies, the president of the Energy Regulatory Office (the competent authority for imposing these fines) may apply a strict approach to fining businesses if they do not limit their natural gas consumption.
How can businesses protect themselves?
The mechanism for imposing restrictions may strike businesses as a surprising anachronism. They may be unaware of the restrictions and thus face severe fines. But they can protect themselves against the negative effects of these restrictions by taking a number of preventive measures. We can divide them into anticipatory and ad hoc measures.
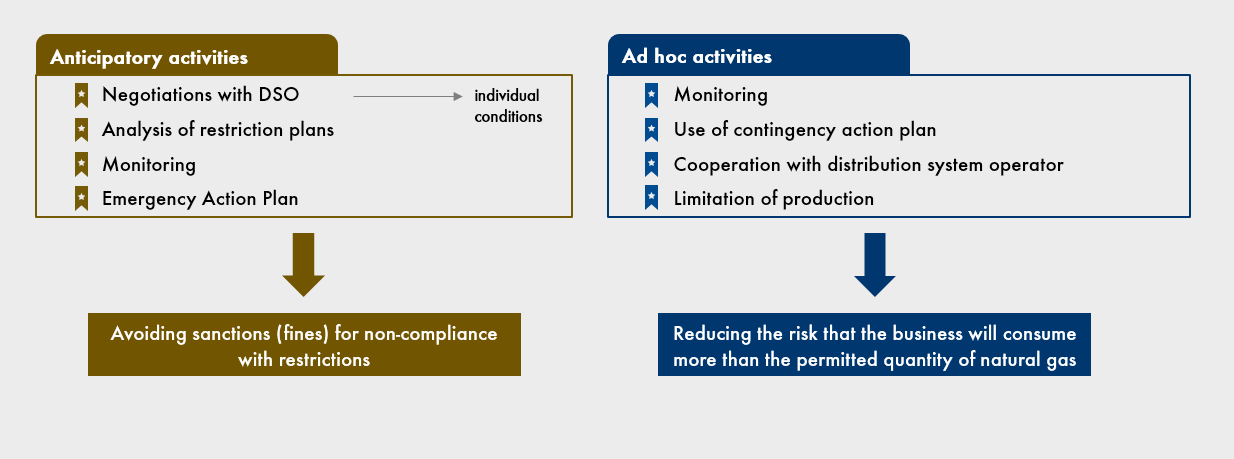
In its business plan or special procedures, every energy market participant consuming natural gas should include mechanisms enabling the best possible protection of its operations against the negative impacts of potential limitations on natural gas consumption.
Igor Hanas, adwokat, Łukasz Bondaruk, adwokat, Energy practice, Wardyński & Partners

